magicGNSS User Terminal is a novel hand-held device which provides a PPP-based positioning and integrity solution to the users.
Welcome to magicGNSS!
magicGNSS suite implements state-of-the-art GNSS algorithms developed by GMV as a result of 25 years' experience in the field. It comprises a set of GNSS tools
Apply for a free account to test our platform!
You can also visit our portfolio to get more information about our products, services and publications!

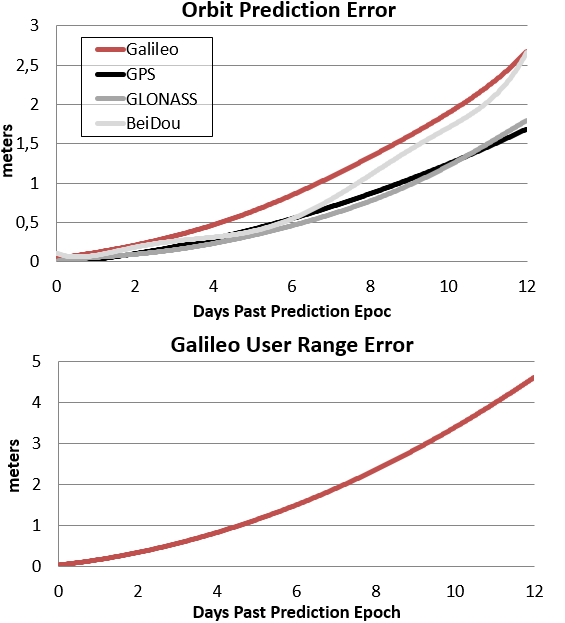
magicEPHEM is a generator of long-term multi-constellation GNSS orbit and clock predictions.
Key Features:
- Multi-constellation
- Hourly updated predictions
- Standard formats (SP3, RINEX)
- Adaptable to specific user needs
Publications
Contact us
Services
Precise Point Positioning by email

Welcome to the email version of magicGNSS/PPP (Precise Point Positioning), now processing static and kinematic GPS, GLONASS and GALILEO real-time data in RINEX format. Only dual-frequency PPP is supported at the moment.
Real-time GPS, GLONASS and GALILEO orbits and clocks needed by PPP are generated internally. Satellite products rate is 1 min. Rapid and final GPS orbits and clocks from IGS are also available. Final IGS clock rate is 30 sec.
Please follow these instructions:
- Send an email to [email protected] with the Subject Static or Kinematic and one RINEX observation file attached (or a maximum of two files for static PPP).
- The attached files must be in standard or Hatanaka RINEX 2.00, 2.10, 2.11, 3.00, 3.01 or 3.02 format, compressed or not.
- The filenames must follow the RINEX filename convention: daily, hourly, high-rate; if your file is compressed, you must keep the RINEX filename extension and the compression extension (for example gap10750.14o.gz)
- The file attached can be an unique compressed file containing more than one RINEX.
- The files can be compressed in the following formats: .Z, .gz and .zip.
- The RINEX data rate must be one of the following, in seconds: 1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 30, 60 and 300.
- The RINEX file must contain all of the following observables: P1 (or C1), P2, L1, L2.
- GPS data earlier than 2009/01/01 and GLONASS/GALILEO data earlier than 2014/01/01 cannot be processed.
- Real-time GPS, GLONASS and GALILEO orbits and clocks
needed by PPP are generated internally. It is possible to force
the use of IGS products writing in the email body:
Products: IGS
In addition, if the products themselves are not available, the IGS products will be used automatically. - In static PPP, if you attach two RINEX files and they belong to the same station, you will also get the comparison of the two PPP results (difference of coordinates).
- Kinematic PPP can be used in two modes: Terrestrial
(default) and Aeronautical. This is configured within
the email body, for example:
To: [email protected]
Subject: Kinematic
Aeronautical - It is possible to process GPS-only and GPS+GLONASS in
PPP. This is configured according to the email Subject:
Static/Kinematic = GPS+GLONASS
Static/Kinematic GR = GPS+GLONASS
Static/Kinematic G = GPS-only - WARNING: emails from the magicGNSS/PPP service might be identified as spam by your email system!