Autonomous integrity
August 4th, 2010 by Ricardo PírizmagicGNSS version 2.5 is now available incorporating the IBPL algorithm supporting GPS+GLONASS. IBPL stands for Isotropy-Based Protection Level, a proprietary algorithm developed by GMV for autonomous pseudorange-based user receiver integrity.
The new IBPL module within magicGNSS is a demonstrator of the IBPL concept, but of course not an operational software, since IBPL is intended to run inside the user receiver.
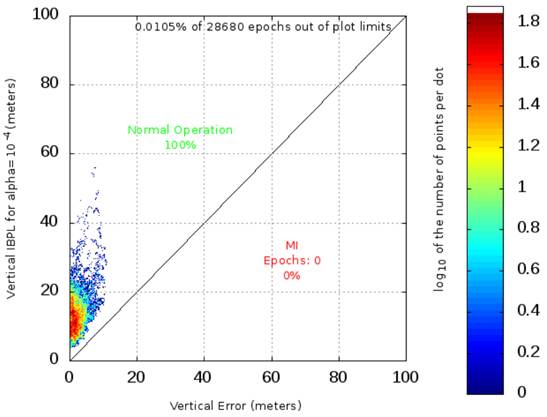
Example of Stanford diagram from IBPL
With the IBPL demonstrator you can upload GPS+GLONASS RINEX observation files and compare code-based user position errors against protection levels from IBPL, and generate integrity statistics (in particular Stanford diagrams). The user position is calculated using a standard single-point algorithm, based on single-frequency code measurements. The true receiver position for the position error calculation comes from Precise Point Positioning.
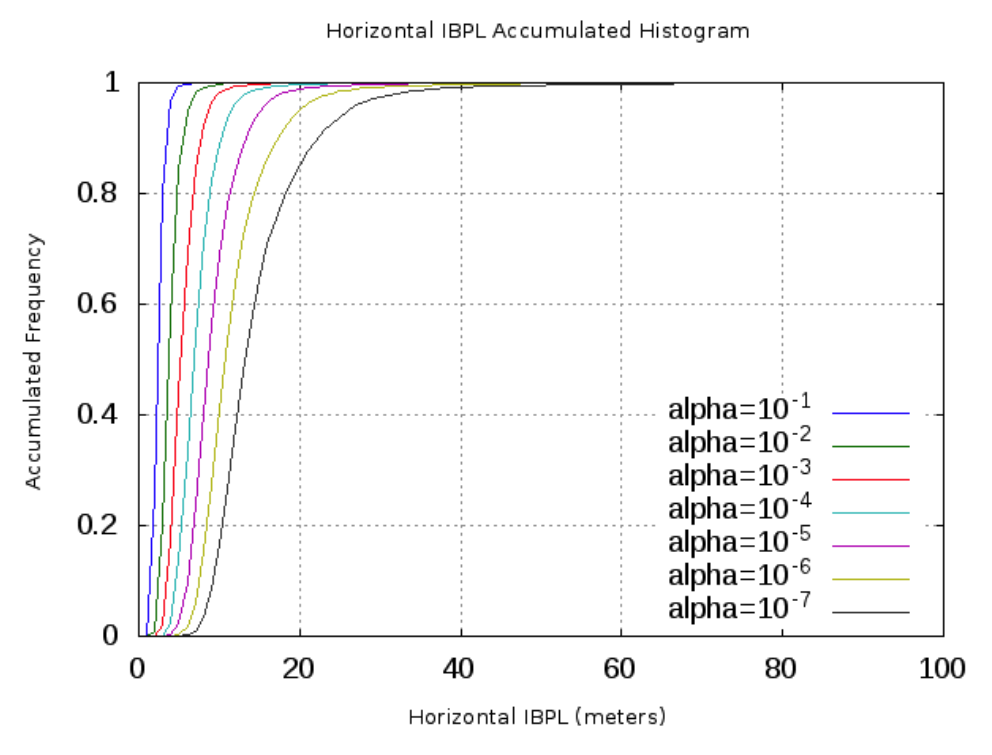
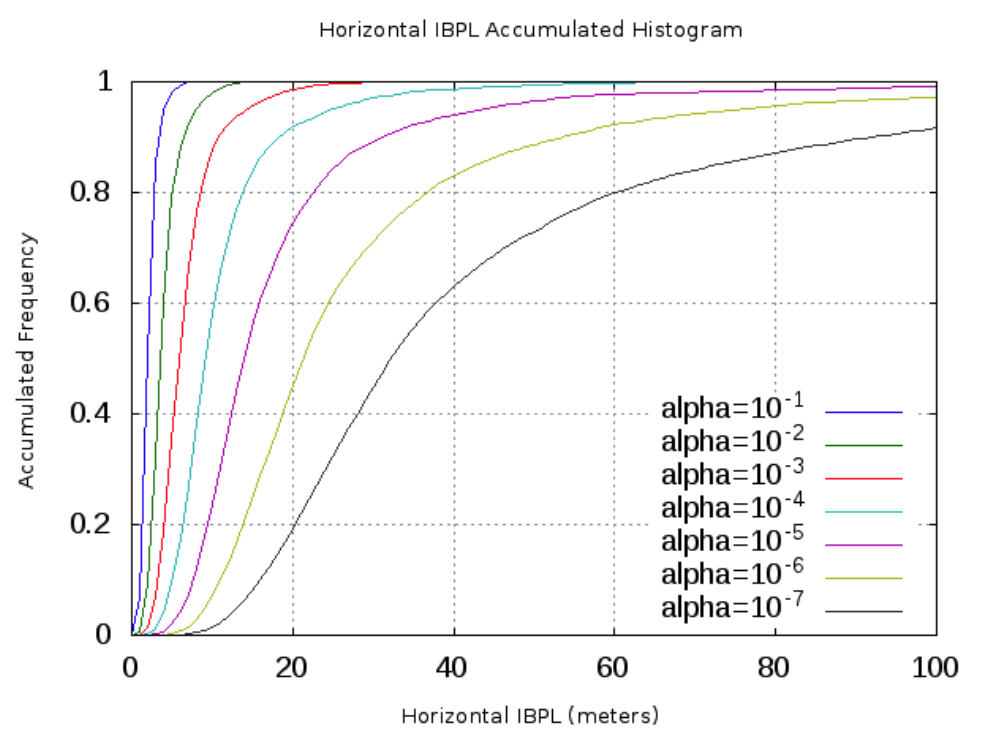
You can also compare the GPS+GLONASS solution against the GPS-only solution, to see how the Protection Level size dramatically decreases when the number of satellites increases. Here is an example for a 7-day open-sky scenario:
You can download the full IBPL report for the previous scenario (GPS+GLONASS case).
REFERENCES:
Integrity in Urban and Road Environments and its use in Liability Critical Applications, J. Cosmen-Schortmann, M. Azaola-Sáenz, M.A. Martínez-Olagüe, M. Toledo-López, GMV (Spain), IEEE/ION PLANS 2008, Monterrey (CA), May 2008.
Isotropy-Based Protection Levels: a Novel Method for Autonomous Protection Level Computation with Minimum Assumptions, Azaola Sáenz, M.; Cosmen Schortmann, J.; Martínez Olagüe, M.A.; Toledo López, M., GMV Aerospace and Defence S.A. (Spain), NAVITEC 2008, Noordwijk (The Netherlands), Dec 2008.
Autonomous Integrity: An Error Isotropy–Based Approach for Multiple Fault Conditions, Joaquín Cosmen-Schortmann, Miguel Azaola-Saenz, InsideGNSS, Jan-Feb 2009. http://www.insidegnss.com/auto/janfeb09-azaoli.pdf