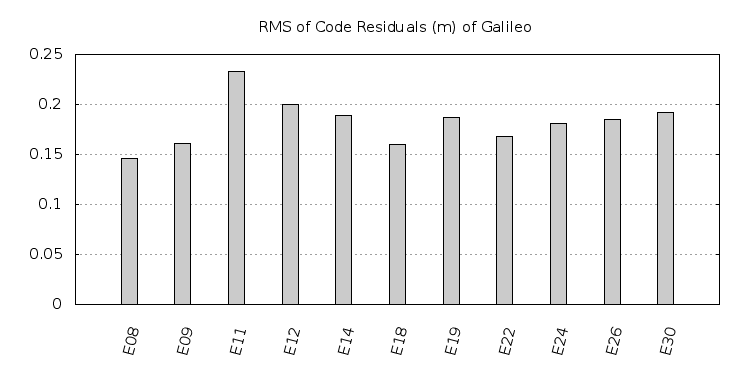
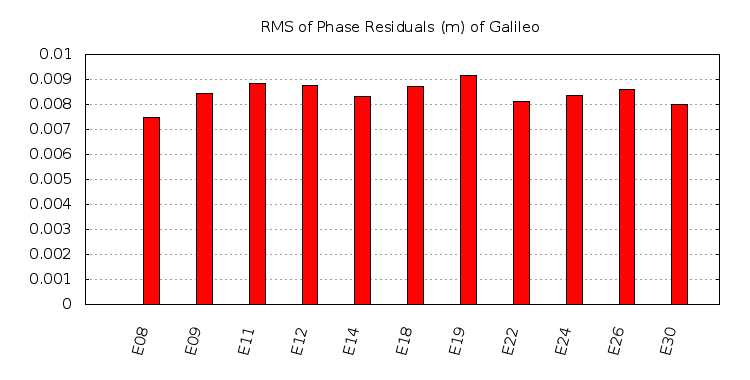
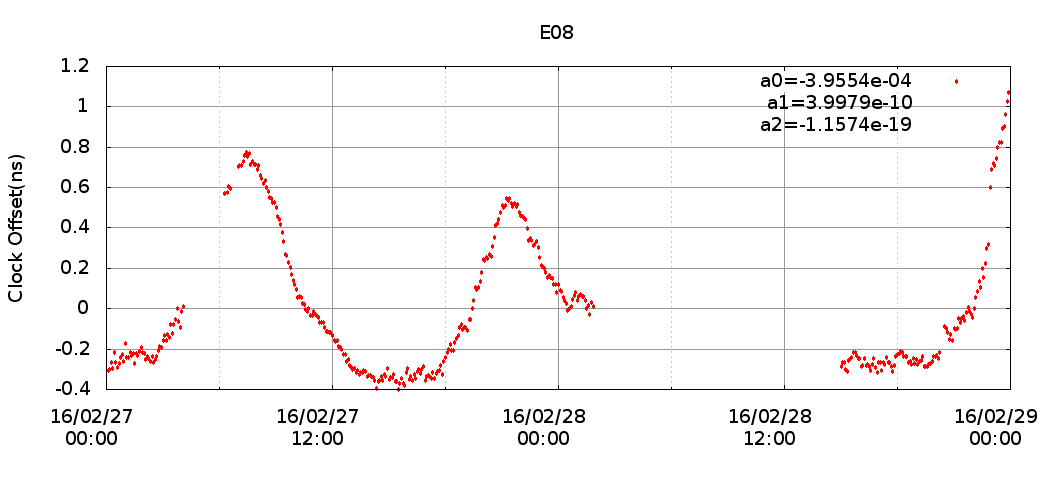
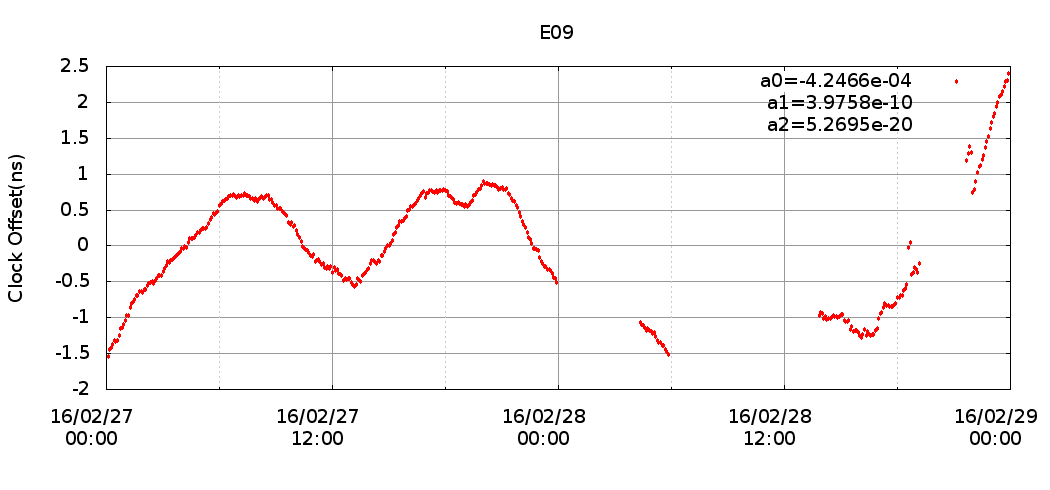
The delay produced by the ionosphere is one of the largest sources of error in GNSS positioning. This error is typically removed by using a dual frequency receiver and processing the ionosphere-free combination. However, the usage of a dual frequency receiver increases the cost of the solution several orders of magnitude.
magicFAST is the new approach implemented in magicGNSS to minimize the impact of the ionospheric delay, even in case single frequency receivers are used. With this approach, a network of ground stations measures the ionospheric delay on a set of strategical positions, and this information is used to provide regional corrections to the users.
As an example of this new functionality, tests with a low-cost U-Blox NEO-M8T receiver have been performed. In these tests, regional corrections computed with a low-density network of stations (with the nearest station at a distance of around 300 km) have been injected in the PPP processing.
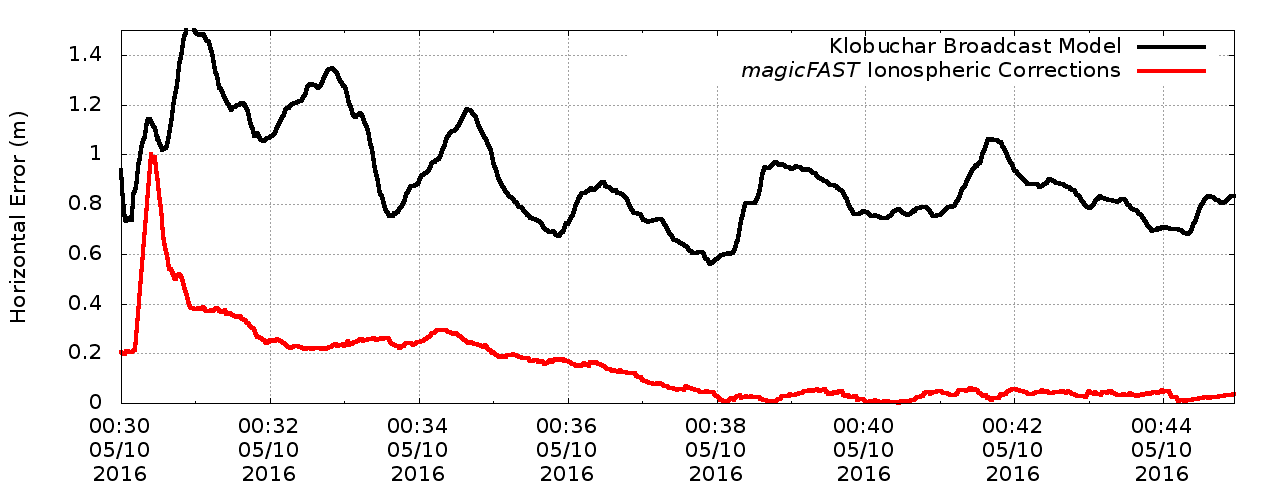
Static open-sky horizontal positioning error
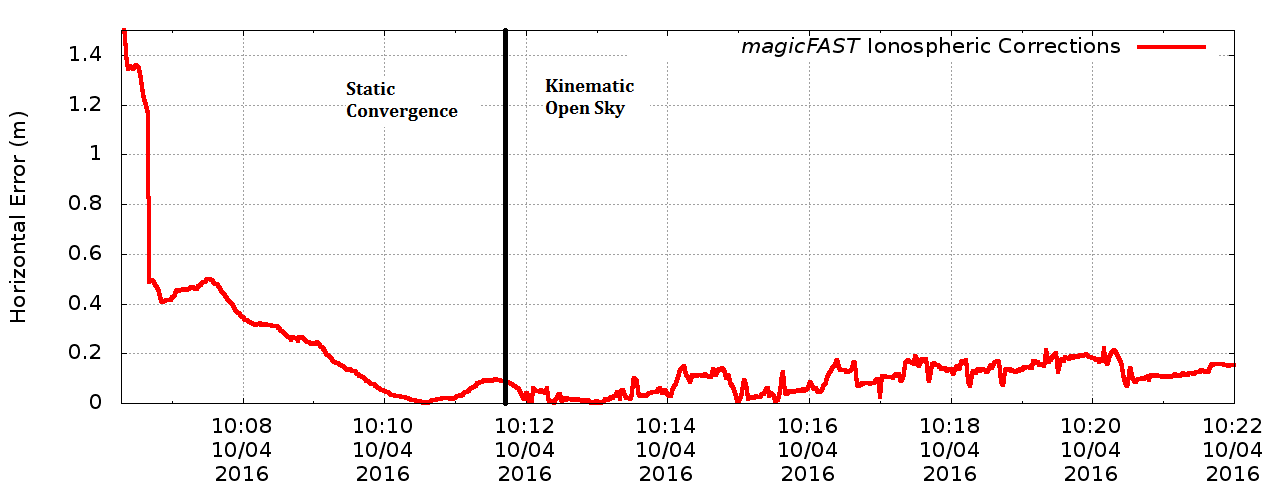
Kinematic open-sky horizontal positioning error
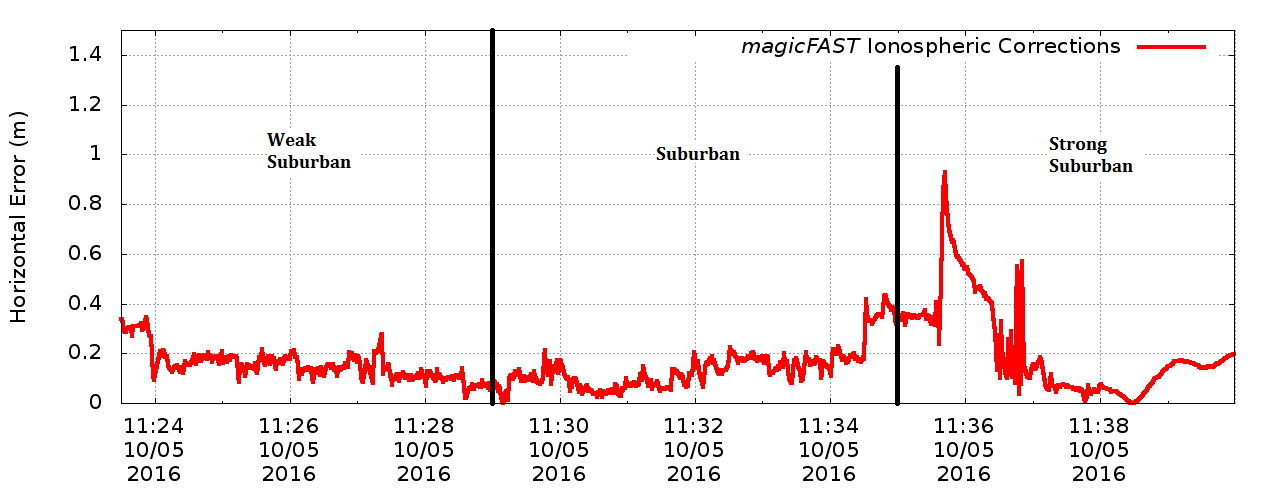
Kinematic suburban horizontal positioning error
The accuracy achieved using magicFAST allows the implementation of features only reached by high-grade receivers, i.e. lane-change detection.
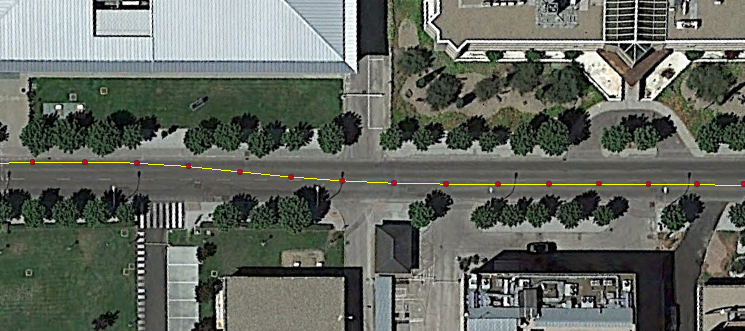
Lane change detection in urban environment
Estimated (red dots) vs. Reference (yellow line) trajectory
It has been found that magicFAST is capable of providing 20cm of positioning accuracy after only 5 minutes of PPP convergence and maintain these performances both in open sky and suburban environments with a low-cost receiver and a patch antenna.